Glycogen phosphorylase often referred to simply as phosphorylase is the enzyme that catalyzes the mobilization of glucose residues from storage in the polymeric form of glycogenThe phosphorolysis of a terminal α-14 linkage phosphate is used to split the linkage results in the production of glucose 1-phosphate and a glycogen chain that is one glucose unit. The activity of this enzyme is positively regulated by AMP and negatively regulated by ATP ADP and glucose-6-phosphate.

Regulation Of Glycogen Phosphorylase And Glycogen Synthase A Glycogen Download Scientific Diagram
This enzyme catalyzes the rate-determining step in glycogen degradation.

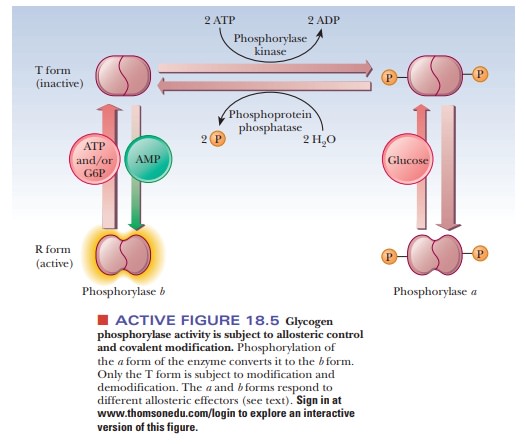
Active form glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen muscle phosphorylase is the main form of GP expressed in glial cells in the human nervous system specifically in astrocytes 202122. The reverse process of dephos-phorylation stimulated by insulin is catalyzed by phospha-tase 1. Glycogen phosphorylase a is the highly active form whereas glycogen phosphorylase b has only limited activity.
To support inhibitor design we determined the crystal structures of the active and inactive forms of human liver glycogen phosphorylase a. Glycogen phosphorylase is a dimmer catalyzing the first and controlled step in glycogen degradation generating glucose 1-phosphate. This transforms it to an active state and it can begin phosphorylating glucose.
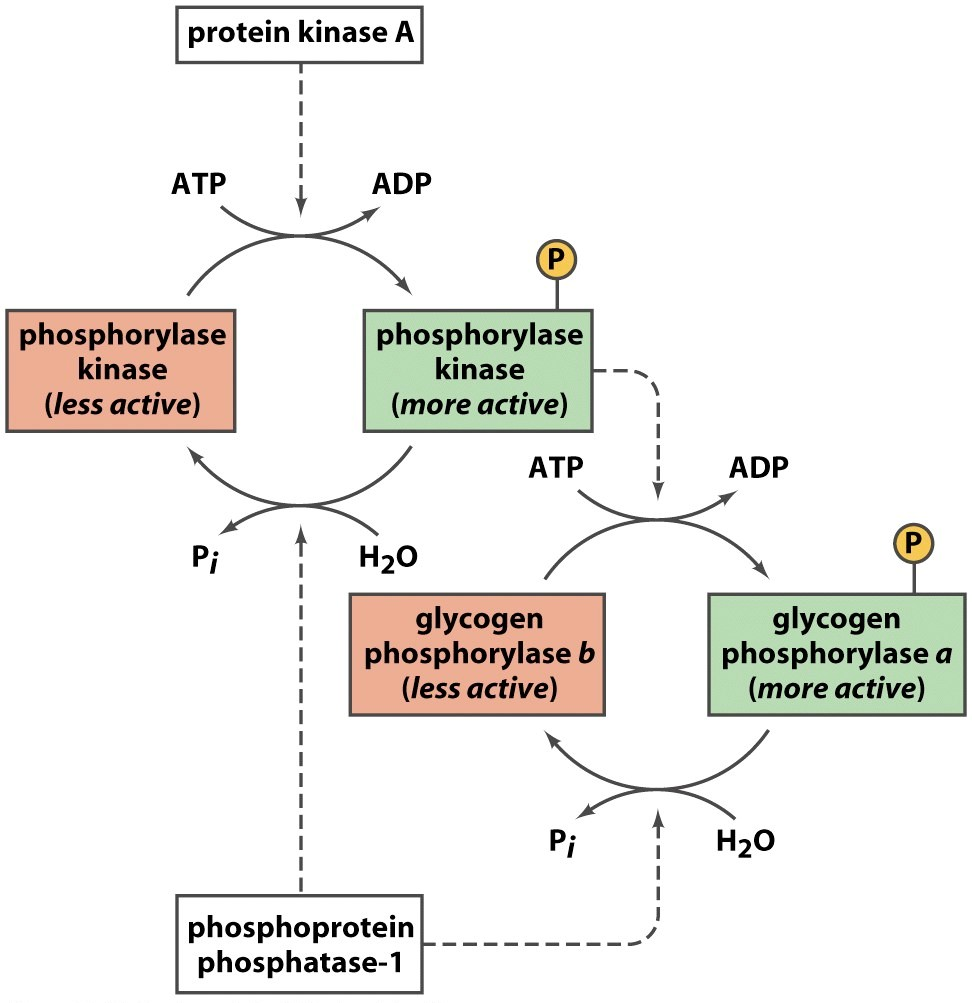
In muscle glycogen phosphorylase is activated by hormones and neural signals such as epinephrine that stimulate phosphorylase kinase which phosphorylates the Ser-14 residue of the protein. Phosphorylase kinase PhK is a serinethreonine-specific protein kinase which activates glycogen phosphorylase to release glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen. The activity of this enzyme is positively regulated by AMP and negatively regulated by ATP ADP and glucose-6-phosphate.
Glycogen synthase 3Glycogen dehydrogenase 4. Refolding of the phosphorylated amino-terminus was shown to create a hydrophobic cluster that wedges into the subunit interface of the enzyme to trigger activation. Options is.
Glycogen phosphorylase is clinically significant enzyme as its mutations are associated with different glycogen storage diseases in muscle and liver. Glycogen phosphorylase is clinically significant enzyme as its mutations are associated with different glycogen storage diseases in muscle and liver. The activated kinase in turn activates the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme by phosphorylating the Ser-14 residue.
Glycogen phosphorylase has two forms one active a form and one inactive b form. The active glycogen phosphorylase kinase then phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase converting it from the inactive tense b form to the active relaxed a form. Why does ATP inhibit glycogen phosphorylase.
Click to see full answer. Thus when glycogen degradation is turned on synthesis is. Phosphatase I inactivates phosphorylase and activates glycogen synthase so that glycogen degradation and.
Glycogen phosphorylase was at least 20-fold less active after incubation of the cells in the presence of glucose but this residual activity had kinetic properties identical to those of the active form of enzyme obtained after incubation in the absence of glucose. During activation forty residues of the catalytic site undergo orderdisorder transitions changes in secondary structure or packing to reorganize the catalytic site for substrate binding and catalysis. By this mechanism epinephrine induces the breakdown of muscle glycogen to supply muscle cells with increased glucose as a ready source of energy to respond to an extant acute stress.
In addition this enzyme has been suggested as a biomarker for gastric cancer and its. A phosphorylation-initiated mechanism of local protein refolding activates yeast glycogen phosphorylase GP. It remains in an inactive form until an inorganic phosphate molecule is added to a serine amino acid group on the enzyme.
The enzyme is in its active form when it is phosphorylated and in its inactive form when de phosphorylated. The cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP cascade action yields the active form of glycogen phosphorylase a which has a phosphoryl group linked to Ser14 in each subunit. PhK phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase at two serine residues triggering a conformational shift which favors the more active glycogen phosphorylase a form over the less active glycogen.
The activated kinase in turn activates the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme by phosphorylating the Ser-14 residue. The phosphorylated threonine is buried in the allosteric site. Phosphorylase B kinase has a pivotal role in both the degradation and the synthesis of glycogen.
This suggests that the b form might be completely inactive and that the low activity measured after glucose treatment. The encoded protein forms homodimers which can associate into homotetramers the enzymatically active form of glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen phosphorylase a is the highly active form whereas glycogen phosphorylase b has only limited activity.
Ated form phosphorylase a GPa is no longer dependent on AMP for activity although the activity of GPa can be aug-mented by AMP about 25. In muscle glycogen phosphorylase is activated by hormones and neural signals such as epinephrine that stimulate phosphorylase kinase which phosphorylates the Ser-14 residue of the protein. Forms of glycogen phosphorylase namely glycogen phosphorylase a and b forms.
The enzyme phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase to an active form while phosphorylating glycogen synthase to an inactive form. The active form of glycogen phosphorylase is phosphorylated while the dephosphorylation of which active form occurs. The majority of the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme a dimer composed of two subunits is bound to the glycogen granule.
The encoded protein forms homodimers which can associate into homotetramers the enzymatically active form of glycogen phosphorylase. PYGM identified by mass spectrometry is also found in T lymphocytes where it plays an important role in their immunological functions 23 24 25 26. Whether the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase is in the active or inactive form is determined by enzymes that either phosphorylate it or dephosphorylate it.

File Glycogen Phosphorylase Kinase Control Png Wikimedia Commons

Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen Metabolism What Is The Importance

Regulation Of Glycogen Metabolism By Glycogen Synthase And Glycogen Download Scientific Diagram
Solved Protein Kinase A Adp Atp Phosphorylase Phosphorylase Chegg Com
Chem 440 Glycogen Phosphorylase

Glycogen Phosphorylase B An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Glycogen Phosphorylase B An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Glycogen Phosphorylase B An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Essential Steps For Glycogenolysis Glycogen Phosphorylase And The Two Download Scientific Diagram
How Is Glycogen Metabolism Controlled

Glycogen Phosphorylase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Glycogen Phosphorylase B An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Glycogen Phosphorylase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Post a Comment
Post a Comment